The well known structure of DNA described above pertains to DNA structure, described by Watson and Crick (1953). Helical coiling of this DNA is assumed to be right handed and this form of DNA has been called B-form. It has been shown that DNA may also exist in other alternative forms of double helical structures. These alternative forms differ in features like (i) number of residues per turn ('
n') or (ii) the spacing of residues along the helical axis ('
h'). The existence of DNA as a double helix has also been confirmed by experiments used to measure the number of base pairs per turn and it has been shown that this is 10.4 instead of 10.0 shown in classical B-form, which is described earlier in this section. This will lead to modification of the twist angle (rotation) between two base pairs from 36° to 34.6° (360°/10.4). This figure of 10.4 base pairs per turn is an average and according to conditions, this may shift in either direction. It is thus obvious that there may be several families of structures of DNA, each of a characteristic type showing variation in the values of
'n' and
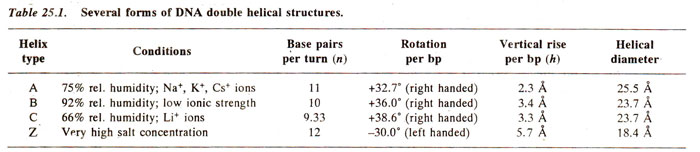
'h' described above. Three structural forms, namely A, B and C are known for a long time and transitions between them can occur. General characteristics of these three forms are given in Table 25.1.
The B-form is found at a very high (92%) relative humidity and low ionic strength. Similarly, A-form is found at 75% relative humidity in the presence of N
+, Ka
+, or Cs
+ ions and C-form is found at 66% relative humidity in the presence of Li
+ (
Lithium)ions. These three forms are assumed to be found in all DNAs.
here are still other forms called D-form and E-form found rarely as extreme variants with only 8 and 7 ½base pairs per turn respectively. These are found only in some DNA molecules lacking guanine. In contrast A, B, and C are found in all DNA molecules irrespective of DNA sequence. As shown in Table 25.1, B DNA is not the only right handed DNA. Similarly, it has been shown that B DNA is not always right handed. B DNA can also be left handed (see RL model later).