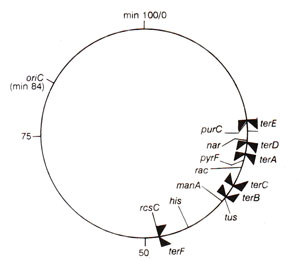
Fig. 26.22. A partial map of E, coli chromosome, showing the position of six termination sites (terA-terF)and the tus gene relative to the location of oriC.
The
E. coli chromosome carries a large termination zone, diametrically opposite from
oriC, which blocks the progress of replication forks (of bidirectional replication), meeting at this region.
E. coli chromosome and several plasmids carry specific sequences, called
ter sites, where
TBP, (ter binding protein) or
'Tus protein' binds. In the termination zone of
E. coli, there are three ter sites (
ter A, ter D and
ter E)for counter-clockwise fork and three
ter sites (
ter B, ter C and
ter F)for clockwise fork. These six sites are arranged in overlapping manner, leaving no 'replication-free' gap on the chromosome (Fig. 26.22). TBP-ter complexes formed at
'ter' sites stalls the replication fork, by inhibiting the DNA helicase or DnaB.When this termination zone is deleted, replication stops simply by the meeting of opposite replication forks, suggesting that the termination zone is not essential.

Fig. 26.22. A partial map of E, coli chromosome, showing the position of six termination sites (terA-terF)and the tus gene relative to the location of oriC.

