Genetics / Organization of Genetic Material / Packaging of DNA as Nucleosomes
Relation between different nucleosomes
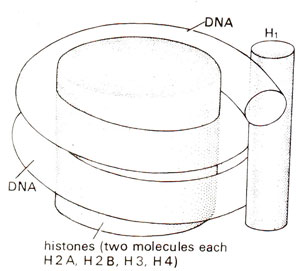
Fig. 27.10. Model of full nucleosome (not the core particle) showing the role of H1 histone, which is attached at the entry and exit of two turns of 166 base pairs long DNA (redrawn from Sci. Amer., Vol. 244, 1981).
The relationship between different nucleosomes was examined on the basis of results of digestion of chromatin by micrococcal nuclease. We have already discussed that the first effect of nuclease is cleavage between nucleosomes which, on prolonged digestion, are reduced to core particles. At an intermediate stage before the core particles are produced, DNA was found to be 166 base pairs long and not 146 base pairs long as in the core particle. When this intermediate stage with 166 base pairs is further degraded to core particle, the histone protein HI is assumed to fall off due to removal of 10 base pairs from each end of DNA.
This suggests that H1 is associated with the ends of DNA molecule. It may also be realized that 166 base pairs will make two complete turns of DNA around the nucleosome, bringing the two ends of DNA as close as possible so that a single molecule of H1 can be bound simultaneously to both the ends of DNA molecule belonging to one nucleosome subunit. In other words, H1 is found on the side of a nucleosome at regions of entry and exit of DNA superhelix, as shown in Figure 27.10. Since H1 is not necessary for coiling of DNA, it is only an accessory protein and may be involved in condensation of chromatin.

Fig. 27.10. Model of full nucleosome (not the core particle) showing the role of H1 histone, which is attached at the entry and exit of two turns of 166 base pairs long DNA (redrawn from Sci. Amer., Vol. 244, 1981).
Support our developers

More in this section





