Genetics / Plasmids, IS Elements, Transposons and Retroelements
Transposons and controlling elements
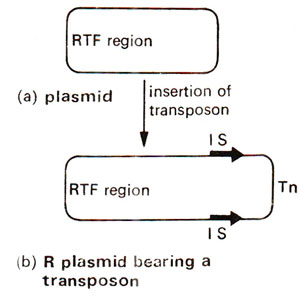
Fig. 15.4. The insertion of a transposon (Tn), including IS elements, into a plasmid (RTF = resistance-transfer factor).
In the previous section, we described insertion sequences, which are capable of moving within the genome through
illegitimate recombination (moving to DNA sequences quite unrelated). In this section, we describe additional extrachromosomal elements, which are transposable and can occupy different sites on the main DNA molecule of plasmid or bacterial chromosome. These elements are popularly described as transposons, both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, in maize these were initially described as
controlling elements, due to their control on the expression of genes. The relationship between plasmid, IS elements and transposons (Tn) is shown in Figure 15.4.

Fig. 15.4. The insertion of a transposon (Tn), including IS elements, into a plasmid (RTF = resistance-transfer factor).
Support our developers

More in this section

