Genetics / Regulation of Gene Expression / Operon Circuits in Prokaryotes
Identification of starting point
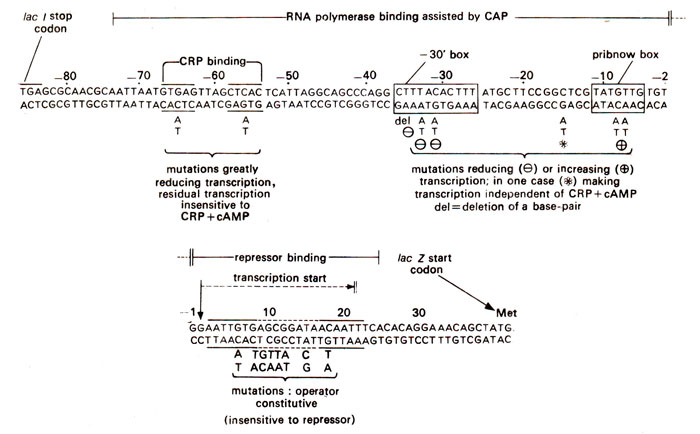
Fig. 35.21. Nucleotide sequence of DNA in E. coli lac transcription control regions, showing functions of different regions and the effects of mutations in these regions.
In the DNA segment sequenced as above, starting point of transcription in
'lac' operon could be identified with the help of S
1 nuclease. This enzyme has the ability to degrade single stranded DNA or RNA, but not DNA-RNA hybrids. Therefore, a DNA restriction fragment (obtained due to treatment with a specific restriction endonuclease) containing the starting point and some transcription region of DNA, was hybridized with excess of
lac mRNA (5' end of mRNA will be complementary to startpoint in DNA) and then digested with S, nuclease. The size of protected duplex DNA-RNA hybrid will determine the position of starting point (upstream) from the downstream restriction site. This sequence used as starting point is shown in Figure 35.21.

Fig. 35.21. Nucleotide sequence of DNA in E. coli lac transcription control regions, showing functions of different regions and the effects of mutations in these regions.
Support our developers

More in this section

