Initiation in eukaryotes
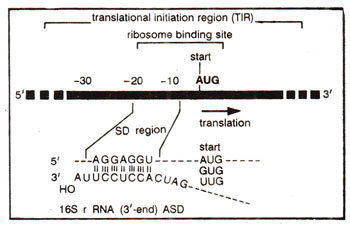
Fig. 34.3. The prokaryotic translational initiation region (TIR), and ribosome binding site (RBS); the Shine-Delgarno region relative to start codon (4-12 bases away) is also shown, which has homology to 3' end of 16S rRNA (ASD region).
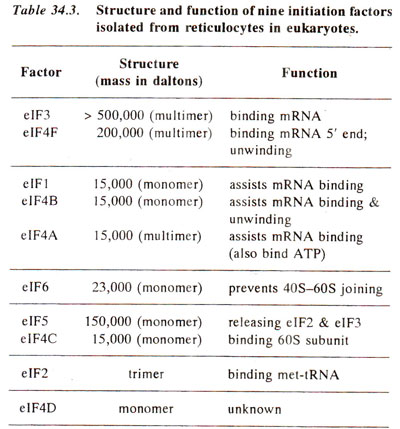
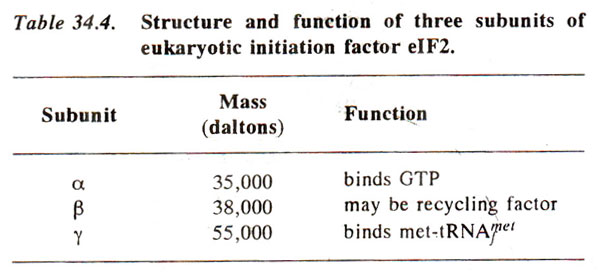
Initiation of polypeptide chain in eukaryotes is similar to that in prokaryotes, except following minor differences, (i) In eukaryotes there are more initiation factors and at least ten have been identified in red blood cells. They are named by putting a prefix 'e' to signify their eukaryotic origin. These factors are eIFl, eIF2, eIF3, eIF4A, eIF4B, eIF4C, eIF4D, eIF4F, eIF5 and eIF6 (Table 34.3). The eIF2, eIF3, eIF4A and eIF4F contain multiple polypeptide chains, but others are single polypeptides; eIF2 and eIF3 are analogous to IF2 and IF3 of prokaryotes. (ii) In eukaryotes, formylation of methionine does not take place, (iii) In eukaryotes, smaller subunit (40S) associates with initiator tRNA known as tRNAimet (because methionine is not formylated), without the help of mRNA, while in prokaryotes, generally the 30S-mRNA complex is first formed, which then associates with f-met-tRNAfmet.
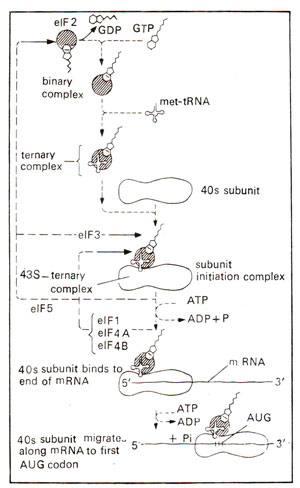
Fig. 34.5. Use of a number of initiation factors in eukaryotes for binding of 40S subunit and mRNA to form a complex. 40S subunit with ternary complex then moves to AUG codon (modified from Lewin's 'Genes').
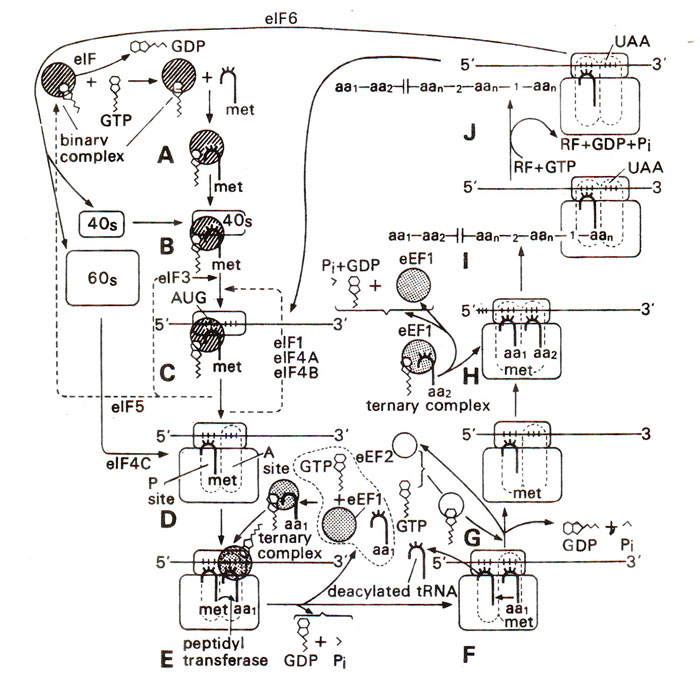
Fig. 34.2. Different steps (A-J) in the translation of mRNA molecule in eukaryotes (reticulocytes).
It should be realized that the initiation process described above is characterized in prokaryotic system by E. coli and in eukaryotic system by red blood cells, where major work has been done. Variations may by found in other systems.

Fig. 34.3. The prokaryotic translational initiation region (TIR), and ribosome binding site (RBS); the Shine-Delgarno region relative to start codon (4-12 bases away) is also shown, which has homology to 3' end of 16S rRNA (ASD region).

Fig. 34.5. Use of a number of initiation factors in eukaryotes for binding of 40S subunit and mRNA to form a complex. 40S subunit with ternary complex then moves to AUG codon (modified from Lewin's 'Genes').

Fig. 34.2. Different steps (A-J) in the translation of mRNA molecule in eukaryotes (reticulocytes).