Genetics / Regulation of Gene Expression / Cricuit of Lytic Cycle and Lysogeny in Bacteriophages
DNA binding of Cro and λ (lambda) repressor proteins
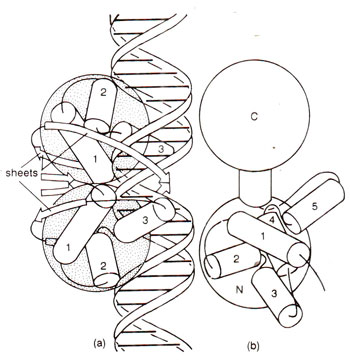
Fig. 36.10. (a) Binding of Cro protein with operator (note that Cro consists of a single domain and its active form is a dimer; each monomer consists of three a helices and a β sheet); (b) N-terminal domain of λrepressor, a helices 2 and 3 are involved in binding DNA).
In the previous topic we discussed the structure of lac repressor and CAP proteins, with respect to its DNA binding properties. A similarity of CAP with Cro and λrepressor proteins, discussed in this section, has also been demonstrated (Table 36.1). Cro consists of a single domain with three
a helices (α, α
2, α
3) and a β sheet. It has a
helix-turn-helix motif that binds the operator symmetrically (Fig. 36.10). λ repressor resembles Cro, but consists of two distinct domains and a connector (as discussed earlier). The N-terminal domain of λrepressor is shown in Figure 36.10. A helix-turn-helix model for DNA binding holds good in this case also. The amino terminal ends form two long arms, which wrap around the DNA (unlike Cro).

Fig. 36.10. (a) Binding of Cro protein with operator (note that Cro consists of a single domain and its active form is a dimer; each monomer consists of three a helices and a β sheet); (b) N-terminal domain of λrepressor, a helices 2 and 3 are involved in binding DNA).
Support our developers

More in this section






