 |
|
Born:
|
July 20, 1822(1822-07-20); Heinzendorf bei Odrau, Austrian Silesia, Austrian Empire
|
|
|
Died:
|
January 6, 1884 (aged 61); Brno, Austria-Hungary
|
|
|
Fields:
|
Genetics
|
|
|
Institutions:
|
Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno
|
|
|
Alma mater:
|
University of Vienna
|
|
|
Known for:
|
Discovering genetics
|
|
|
Religious stance:
|
Roman Catholic
|
|
Gregor Johann Mendel |
|
|
Gregor Johann Mendel (July 20, 1822 – January 6, 1884) was a Austrian Augustinian priest and scientist, and is often called the father of genetics for his study of the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants. Mendel showed that the inheritance of these traits follows particular laws, which were later named after him. The significance of Mendel's work was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century. Its rediscovery prompted the foundation of the discipline of genetics.
Biography
Mendel was born into a ethnic German family in Heinzendorf bei Odrau, Austrian Silesia, Austrian Empire (now Hynčice, Czech Republic), and was baptized two days later. He was the son of Anton and Rosine Mendel, and had one older sister and one younger. They lived and worked on a farm which had been owned by the Mendel family for at least 130 years. During his childhood, Mendel worked as a gardener, studied beekeeping, and as a young man attended the Philosophical Institute in Olomouc in 1840–1843. Upon recommendation of his physics teacher Friedrich Franz, he entered the Augustinian Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno in 1843. Born Johann Mendel, he took the name Gregor upon entering monastic life. In 1851 he was sent to the University of Vienna to study, returning to his abbey in 1853 as a teacher, principally of physics.
Gregor Mendel, who is known as the "father of modern genetics", was inspired by both his professors at university and his colleagues at the monastery to study variation in plants, and he conducted his study in the monastery's garden. Between 1856 and 1863 Mendel cultivated and tested some 29,000 pea plants (i.e. Pisum sativum). This study showed that one in four pea plants had purebred recessive alleles, two out of four were hybrid and one out of four were purebred dominant. His experiments brought forth two generalizations, the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, which later became known as Mendel's Laws of Inheritance.
Mendel read his paper, "Experiments on Plant Hybridization", at two meetings of the Natural History Society of Brünn in Moravia in 1865. When Mendel's paper was published in 1866 in Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn, it had little impact and was cited about three times over the next thirty-five years. His paper was criticized at the time, but is now considered a seminal work.
After Mendel completed his work with peas, he turned to experimenting with honeybees, in order to extend his work to animals. He produced a hybrid strain (so vicious they were destroyed), but failed to generate a clear picture of their heredity because of the difficulties in controlling mating behaviours of queen bees. He also described novel plant species, and these are denoted with the botanical author abbreviation "Mendel".
Elevated as abbot in 1868, his scientific work largely ended as Mendel became consumed with his increased administrative responsibilities, especially a dispute with the civil government over their attempt to impose special taxes on religious institutions.
At first Mendel's work was rejected, and it was not widely accepted until after he died. The common belief at the time was that Darwin's theory of pangenes were responsible for inheritance. The modern synthesis uses Mendelian genetics.
Mendel died on January 6, 1884, at age 61, in Brünn, Austria-Hungary (now Brno, Czech Republic), from chronic nephritis. Czech composer Leoš Janáček played the organ at his funeral. After his death the succeeding abbot burned all papers in Mendel's collection, to mark an end to the disputes over taxation.
Rediscovery of Mendel's work
It was not until the early 20th century that the importance of his ideas was realized. In 1900, his work was rediscovered by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns. Though Erich von Tschermak was originally also credited with rediscovery, this is no longer accepted because he did not understand Mendel's laws. Mendel's results were quickly replicated, and genetic linkage quickly worked out. Biologists flocked to the theory, even though it was not yet applicable to many phenomena, it sought to give a genotypic understanding of heredity which they felt was lacking in previous studies of heredity which focused on phenotypic approaches. Most prominent of these latter approaches was the biometric school of Karl Pearson and W.F.R. Weldon, which was based heavily on statistical studies of phenotype variation. The strongest opposition to this school came from William Bateson, who perhaps did the most in the early days of publicising the benefits of Mendel's theory (the word "genetics", and much of the discipline's other terminology, originated with Bateson). This debate between the biometricians and the Mendelians was extremely vigorous in the first two decades of the twentieth century, with the biometricians claiming statistical and mathematical rigor, whereas the Mendelians claimed a better understanding of biology. In the end, the two approaches were combined as the modern synthesis of evolutionary biology, especially by work conducted by R. A. Fisher as early as 1918.
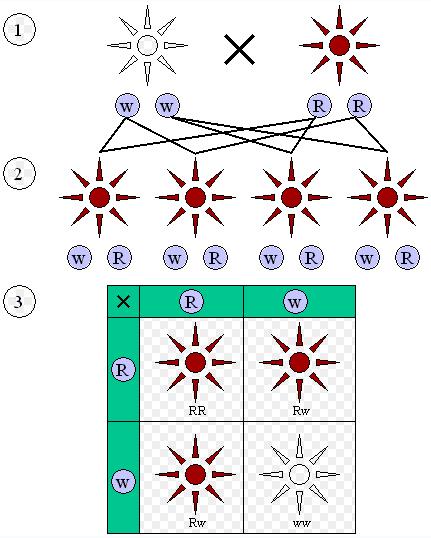 |
Dominant and recessive phenotypes. (1) Parental generation. (2) F1 generation. (3) F2 generation. |
Mendel's experimental results have later been the object of considerable dispute. Fisher analyzed the results of the F2 (second filial) ratio and found them to be implausibly close to the exact ratio of 3 to 1. Only a few would accuse Mendel of scientific malpractice or call it a scientific fraud — reproduction of his experiments has demonstrated the validity of his hypothesis — however, the results have continued to be a mystery for many, though it is often cited as an example of confirmation bias. This might arise if he detected an approximate 3 to 1 ratio early in his experiments with a small sample size, and continued collecting more data until the results conformed more nearly to an exact ratio. It is sometimes suggested that he may have censored his results, and that his seven traits each occur on a separate chromosome pair, an extremely unlikely occurrence if they were chosen at random. In fact, the genes Mendel studied occurred in only four linkage groups, and only one gene pair (out of 21 possible) is close enough to show deviation from independent assortment; this is not a pair that Mendel studied.
Gallery
Bibliography
- Cheryl Bardoe Gregor Mendel: The Friar who grew peas., HN Abrams, 2006.
- William Bateson Mendel's Principles of Heredity, a Defense, First Edition, London: Cambridge University Press, 1902. On-line Facsimile Edition: Electronic Scholarly Publishing, Prepared by Robert Robbins
- Robin Marantz Henig, Monk in the Garden: The Lost and Found Genius of Gregor Mendel, the Father of Genetics, Houghton Mifflin, May, 2000, hardcover, 292 pages, ISBN 0-395-97765-7; trade paperback, Houghton Mifflin, May, 2001.
- Robert Lock, Recent Progress in the Study of Variation, Heredity and Evolution, London, 1906
- Vítězslav Orel, Gregor Mendel: the first geneticist, Oxford University Press. 1996.
- Reginald Punnett, Mendelism, Cambridge, 1905
- Curt Stern and Sherwood ER (1966) The Origin of Genetics.
- Colin Tudge In Mendel's footnotes ISBN 0-09-928875-3 book about Gregor Mendel
- Bartel Leendert van der Waerden Mendel's experiments Centaurus 12, 275-288 (1968) refutes allegations about "data smoothing"
- James Walsh, Catholic Churchmen in Science, Philadelphia: Dolphin Press, 1906
- Ronald A. Fisher, "Has Mendel's Work Been Rediscovered?" Annals of Science, Volume 1, (1936): 115-137. Discusses the possibility of fraud in his research.