Germplasm theory
Germplasm theory of Weismann was a very significant advancement in our understanding of heredity, since this was for the first time that a distinction between hereditary and environmental variations could be made on a sound basis.
The nature of horticulture

Horticulture may be described as the practice of growing plants in a relatively intensive manner. This contrasts with agriculture, which, in most Western European countries, relies on a high level of machinery use over an extensive area of land
Distribution of Life on Earth
The biosphere as usually defined is the thin outer layer of the earth capable of supporting life. It is probably best viewed as a global system that includes all life on earth and the physical environments in which living organisms exist and interact.
Kingdom Plantae
Plants appeared on land about 425 million years ago and the evolutionary history of the plant kingdom reflects increasing adaptation to the terrestrial environment. Plants have organs and organ systems.
Structural bioinformatics
Structural bioinformatics is concerned with computational approaches to predict and analyse the spatial structure of proteins and nucleic acids.
Cultures of Microorganisms
Microorganisms isolated from different sources (soil, water and air) or genetic manipulation are cultured on growth media.
Agriculture Biotechnology
Biotechnology can be seen as an imprecise term since the harnessing of any biological process could justifiably be called biotechnology.
Atomic spectroscopy
Atoms of certain metals will absorb and emit radiation of specific wavelengths when heated in a flame, in direct proportion to the number of atoms present.
Types of Tissues
A tissue is a group of similar cells (together with associated cell products) specialized for the performance of a common function.
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are classified according to the amino acid that provides both the nitrogen atom and the fundamental portion of the alkaloid skeleton, and these are discussed in turn.
Developmental genetics
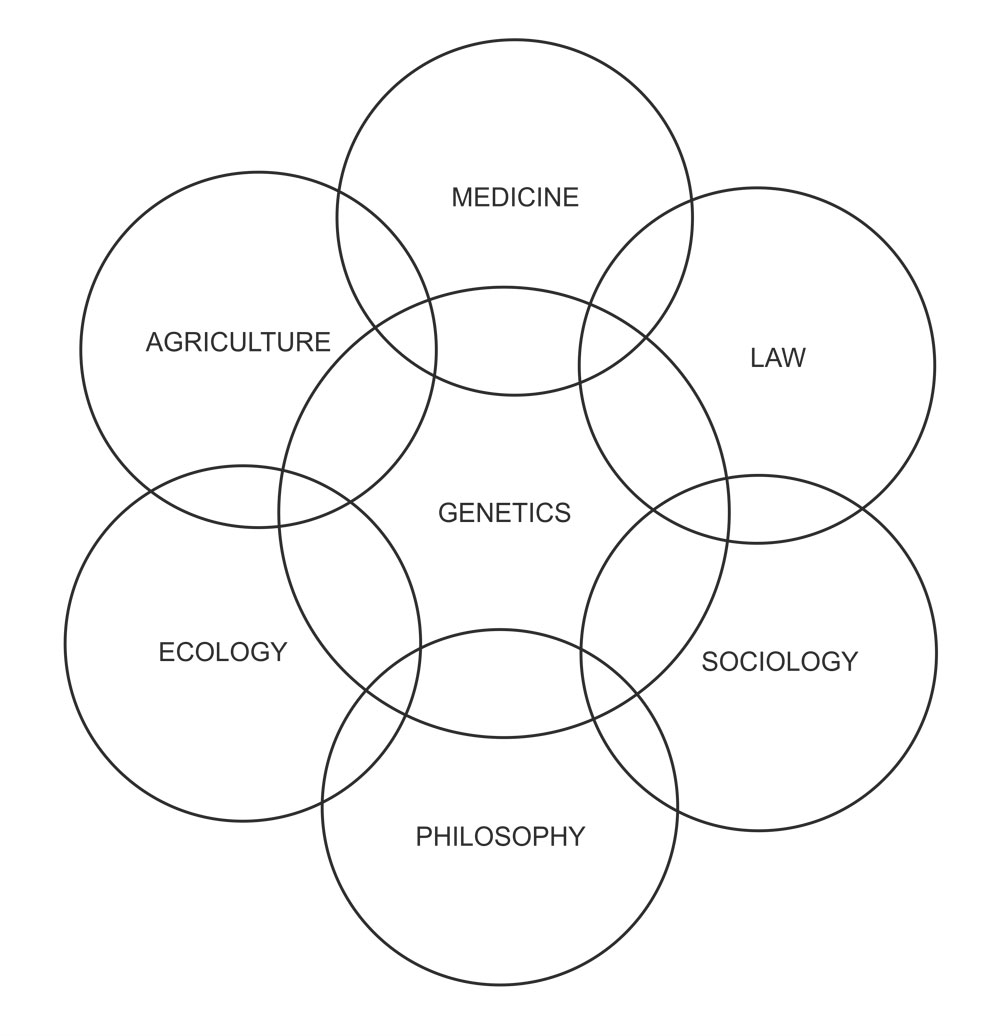
The area of developmental genetics has also received major attention of geneticists in recent years to answer questions like the following. What are the relative roles of nucleus and cytoplasm in differentiation?
Ameboid Movement
Ameboid movement is a form of movement especially characteristic of amebas and other unicellular forms; it is also found in many wandering cells of metazoans, such as white blood cells, embryonic mesenchyme, and numerous other mobile cells that move throu
Evolution of Nervous Systems
Bilateral nervous systems, the simplest of which occur in flatworms, represent a distinct increase in complexity over the nerve net of radiate animals.
Types of Mutations
Mutations are heritable changes in the genetic material that give rise to alternative forms of any gene. These alternate forms are called alleles. There are two broad types of mutations, those that affect the gene and those that affect whole chromosomes (
Bioenergetics
An amalgamation of the term biological energetics, is the branch of biology and biochemistry that is concerned with how organisms extract energy from their environment and with how energy is used to fuel the myriad of life?s endergonic processes.
Natural Antioxidants in Foods
To protect food quality and safety, antioxidants are often added to processed foods. These antioxidants can be synthetically derived compounds, such as butylated hydroxytoluene and ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid.




