Preparation of Reagents and Media
Reagents for various determinations are prepared as follows:
-
Alkalinity
- 0.02 N standard sulphuric acid: Prepare stock solution approximately 0.1 N by diluting 2.5 mL concentrated sulphuric acid to 1 litre. Dilute 200 mL of the 0.1 N stock solution to 1 litre CO2 free distilled water. Standardise the 0.02 N acid against a 0.02 N sodium carbonate solution which has been prepared by dissolving 1.06 g anhydrous Na2CO3 and diluting to the mark of a 1 litre volumetric flask.
- Methyl orange indicator: Dissolve 500 mg methyl orange powder in distilled water and dilute it to 1 litre. Keep the solution in dark or in an amber coloured bottle.
- Phenolphthalein indicator: Dissolve 5 g phenolphthalein in 500mL ethyl alcohol and add 500 mL distilled water. Then add 0.02 N sodium hydroxide drop-wise until a faint-pink colour appears.
- Sodium thiosulphate 0.1 N: Dissolve 25 g Na2S2O3.5H2O and dilute to 1 litre.
- Ammonia buffer solution: Dissolve 16.9 g ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) in 143 mL concentrated ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). Add 1.25 g magnesium salt of EDTA and dilute to 250 mL with distilled water. Do not store more than a month's supply. Discard the buffer when 1 or 2 mL added to the sample fails to produce a pH of 10.0±0.1 at the end point of titration. Keep the solution in a plastic or resistant glass container.
- Eriochrome black T indicator: Mix 0.5 g Eriochrome black T dye with 4.5 g hydroxylamine hydrochloride. Dissolve this mixture in 100 ml of 95% ethyl or isopropyl alcohol.
- Standard EDTA titrant 0.01 M: Weigh 3.723 g analytical reagent grade EDTA disodium salt (Na2H2C10H12O8N2) and dissolve in distilled water and dilute to 1litre.
- Potassium chromate indicator: Dissolve 50 g potassium chromate (K2Cr2O4) in a little distilled water.Add silver nitrate solution until a definite red precipitate is formed. Let stand for 12 hours, filter and dilute the filtrate to 1 litre with distilled water.
- Standard silver nitrate solution 0.0141 N: Dissolve 2.395 g AgNO3 in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre. Standardise against 0.0141 N NaCl. Store in a brown bottle; 1 mL = 500 µg Cl2.
- Standard sodium chloride 0.0141N: Dissolve 824.1 mg NaCl (dried at 140°C) in chloride free water and dilute to 1 litre. 1mL = 500 µg Cl2.
- Aluminium hydroxide suspension: Dissolve 125 g aluminium potassium sulphate in 1 litre water. Warm to 60°C and add 55 mL concentrated NH4OH slowly with stirring. Let stand for 1 hour, transfer the mixture to a large bottle. When freshly prepared the suspension occupies a volume of approximately 1 litre.
- Hydrochloric acid: Concentrated HCl.
- Hydroxylamine solution: Dissolve 10 g hydroxylamine hydrochloride salt (NH2OH.HCl) in 100 mL distilled water.
- Ammonium acetate buffer solution: Dissolve 250 g ammonium acetate (NH4C2H3O2) in 150 mL distilled water. Add 700 mL concentrated (glacial) acetic acid.
- Sodium acetate solution: Dissolve 200 g sodium acetate (NaC2H3O2.3H2O) in 800 mL distilled water.
- Phenanthroline solution: Dissolve 100 mg 1, 10-phenanthroline monohydrate (C12H8N2.H2O) in 100 mL distilled water by stirring and heating to 80°C. Do not boil. Discard the solution if it darkens. Heating is unnecessary if 2 drops of concentrated HCl are added to the distilled water. 1 mL of this reagent is sufficient for no more than 100 µg Fe.
- Stock iron solution: Add slowly 20 mL concentrated H2SO2 to 50 mL distilled water and dissolve 1.404 g ferrous ammonium sulphate [Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2.6H2O]. Add 0.1 N KMnO4 drop wise until a faint-pink colour persists. Dilute to 1litre with iron free distilled water. Each 1 mL of this solution contains 200 µg Fe.
- Standard iron solution: Pipette 50 mL stock solution into 1 litre volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with distilled water. 1 mL = 10 µg Fe.
- Special reagent: Dissolve 75 g mercuric sulphate (HgSO4) in 400 mL concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and 200 mL distilled water. Add 200 mL 85% phosphoric acid and 35 mg silver nitrate to the above solution. Dilute the cooled solution to 1 litre.
- Ammonium persulphate: (NH4)2S2O3 solid.
- Standard manganese solution: Prepare a 0.1 N potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solution by dissolving 3.2 g of KMnO4 in distilled water and making it up to 1 litre. Age for several days in sunlight or heat for several hours near the boiling point and then filter through fritted glass filter crucible and standardise against sodium oxalate. Calculate the volume of this solution necessary to prepare 1 litre solution of such strength that 1mL = 50 µg Mn as follows:
- Conditioning reagent: Mix 50 mL glycerol with a solution containing 30 mL concentrated HCl, 300 mL distilled water, 100 mL 95% ethyl or isopropyl alcohol and 75 g NaCl.
- Barium chloride: Barium chloride crystals.
- Standard sulphate solution: Prepare a standard sulphate solution such that 1 mL = 100 µg SO4. Dissolve 147.9 mg anhydrous Na2SO4 in 500 mL distilled water and dilute to 1 litre 1 mL = 100 µg SO4.
- Hydrochloric acid: Prepare a 6 N solution.
- Standard iodine solution 0.025 N: Dissolve 20 - 25 g potassium iodide in a little water and add 3.2 g iodine. After the iodine has dissolved, dilute to 1 litre and standardise against 0.025 N sodium thiosulphate using starch as indicator.
- Standard sodium thiosulphate 0.025 N: Dissolve 6.205 g sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3.5H2O) in freshly boiled and cooled distilled water and dilute to 1litre. Preserve by adding 5mL chloroform or 0.4 g NaOH/L or 4 g borax and 5 - 10 mg HgI2/L. Standardise this with 0.025 N potassium dichromate solution which is prepared by dissolving 1.226 g potassium dichromate in distilled water and diluted to 1 litre.
- Starch indicator: Add cold water suspension of 5 g soluble starch to approximately 800 mL boiling water with stirring. Dilute to 1 litre, allow to boil for a few minutes and let settle overnight. Use supernatant liquor. Preserve with 1.25 g salicylic acid/litre or by the addition of a few drops of toluene.
- Manganous sulphate solution: Dissolve 480 g MnSO4.4H2O, 400 g MnSO2.2H2O or 364 g MnSO4.H2O in distilled water, filter and dilute to 1 litre.
- Alkali-iodide-azide reagent: Dissolve 500 g NaOH or 700 g KOH and 135 g NaI or 150 g KI in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre. Add 10 g sodium azide (NaN3) dissolved in 40 mL distilled water. The reagent should not give colour with starch when diluted and acidified.
- Sulphuric acid concentrated: 1mL is equivalent to about 3 mL alkali-iodide-azide reagent.
- Standard sodium thiosulphate 0.025 N: Dissolve 6.205 g sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3.5H2O) in freshly boiled and cooled distilled water and dilute to 1 litre. Preserve by adding 5 mL chloroform or 0.4 g NaOH/L or 4 g borax and 5 - 10 mg HgI2/L. Standardise this with 0.025 N potassium dichromate solution which is prepared by dissolving 1.226 g potassium dichromate in distilled water and diluted to 1 litre.
- Standard potassium dichromate solution 0.025 N: A solution of potassium dichromate equivalent to 0.025 N sodium thiosulphate contains 1.226 g/L K2Cr2O7. Dry K2Cr2O7 at 103°C for 2 hrs before making the solution.
- Standardisation of 0.025 N sodium thiosulphate solution: Dissolve approximately 2 g KI in an Erlenmeyer flask with 100 to 150 mL distilled water. Add 10 mL of H2SO4, followed by exactly 20 mL, 0.1 N potassium dichromate solution. Place in the dark for 5 minutes, dilute to approximately 400 mL and titrate with 0.025 N sodium thiosulphate solution, adding starch towards the end of titration. Exactly 20 ml 0.025 N thiosulphate will be consumed at the end of the titration. Otherwise, the thiosulphate solution should be suitably corrected.
- Starch Indicator: Add cold water suspension of 5 g soluble starch to approximately 800 mL boiling water with stirring. Dilute to 1 litre, allow to boil for a few minutes and let settle overnight. Use supernatant liquor. Preserve with 1.25 g salicylic acid/1 litre or by the addition of a few drops of toluene.
- Phosphate buffer solution: Dissolve 8.5 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4), 21.75 g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4), 33.4 g disodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate (Na2HPO4.7H2O) and 1.7 g NH4Cl in about 500 ml distilled water and dilute to 1 litre. The pH of this buffer should be 7.2 without further adjustment. Discard the reagent if there is any sign of biological growth in the stock bottle.
- Magnesium sulphate solution: Dissolve 22.5 g MgSO4.7H2O in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre.
- Calcium chloride solution: Dissolve 27.5 g anhydrous CaCl2 in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre.
- Ferric chloride solution: Dissolve 0.25 g FeCl3.6H2O in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre.
- Sodium sulphate solution 0.025 N: Dissolve 1.575 g anhydrous Na2SO3 in 1 litre distilled water. This is to be prepared daily.
- Seeding: The standard seed material is settled domestic wastewater that has been stored at 20°C for 24 to 36 hours. A seed concentration of 1-2 mL/L is usually adopted.
- Dissolve 1.35 g orthotolidine dihydrochloride in 500 mL distilled water: Add this solution with constant stirring to a mixture of 350 mL distilled water and 150 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid. Store the solution in brown bottle. Always use an automatic, dropping or safety pipette to measure the necessary volume. Avoid inhalation or exposure to the skin.
- Lactose broth: Beef extract 3 g, peptone 5 g, lactose 5 g and reagent grade distilled water 1 litre. Add these ingredients to reagent grade distilled water, mix thoroughly and heat to dissolve. pH should be 6.8 - 7.0 after sterilisation.
- Lauryl tryptose broth: Tryptose 20 g, lactose 5 g, K2HPO4 2.75 g, KH2PO4 2.75 g, NaCl 5 g, sodium lauryl sulphate 0.1 g, reagent grade distilled water 1 litre, sterilise and use. Add dehydrated ingredients to water, mix thoroughly and heat to dissolve. pH should be 6.8 ±2 after sterilisation.
- Endo agar: Peptone 10 g, lactose 10 g, K2HPO4 3.5 g, agar 15 g, sodium sulphite 2.5 g, basic fuchsin 0.5 g, distilled water 1 litre, pH 7.4 after sterilisation.
- EMB agar: Peptone 10 g, lactose 10 g, K2HPO4 2 g, agar 15 g, eosin 0.4 g, methylene blue 0.065 g, distilled water 1 litre, pH should be 7.1 after sterilisation.
- Brilliant green lactose bile broth: Peptone 10 g, lactose 10 g, oxgall 20 g, brilliant green 0.0133 g, distilled water 1 litre, pH should be 7.2 after sterilisation and is then ready for use. Store away from direct sunlight to extend the reagent stability to 6 months.
- NaOH solution 0.02 N: Dissolve 4 g NaOH in 1 litre water. This gives 0.1 N NaOH solution. Take 200 ml of this 0.1 N solution and make it up to 1 litre to obtain 0.02 N NaOH solution.
- Methyl orange indicator: Dissolve 500 mg methyl orange powder in distilled water and dilute it to 1 litre.
- Phenolphthalein indicator: Dissolve 5 g phenolphthalein disodium salt in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre.
- Sodium thiosulphate 0.1 N: Dissolve 25 g Na2S2O3.5H2O and dilute to 1 litre distilled water.
- Standard potassium dichromate solution 0.25 N: Dissolve 12.259 g K2Cr2O7primary standard grade previously dried at 103°C for 2 hours and dilute to 1 litre.
- Sulphuric acid reagent: Concentrated H2SO4 containing 22 g silver sulphate per 4 kg bottle.Dissolve 22 g Ag2SO2 in 4 kg bottle and keep it for 2 days. This is the reagent.
- Standard ferrous ammonium sulphate 0.1 N: Dissolve 39 g Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2.6H2O in distilled water. Add 20 mL conc. H2SO4 and cool and dilute to 1 litre. Standardise this against the standard dichromate solution. Dilute 10 mL standard K2Cr2O7 solution to about 100 mL. Add 30 mL conc. H2SO4 and cool. Titrate with ferrous ammonium sulphate titrant using 2 - 3 drops of ferroin indicator.
- Zinc sulphate solution: Dissolve 100 g ZnSO4.7H2O and dilute to 1 litre.
- EDTA reagent (stabiliser): Dissolve 50 g EDTA disodium salt in 60 mL of water containing 10 g NaOH.
- Nessler's reagent: Dissolve 100 g HgI2 and 70 g KI in a small quantity of water and add this mixture slowly with stirring to a cool solution of 160 g NaOH in 500 mL water. Dilute to 1 litre and store in rubber stoppered pyrex glass out of sunlight.
- Stock ammonia solution: Dissolve 3.811 g anhydrous NH4Cl dried at 100°C in water and dilute to 1 litre. 1 mL = 1.00 mg N and 1.22 mg NH3.
- Stock nitrate solution: Dissolve 721.8 mg anhydrous potassium nitrate and dilute to 1 litre with distilled water. 1 mL = 0.1 mg N.
- Standard nitrate solution: Dilute 10 mL stock nitrate solution to 1 litre. 1 mL = 1 µg N
- Sodium arsenite solution: Dissolve 5.0 g NaAsO2 and dilute to 1 litre.
- Brucine-sulphanilic acid solution: Dissolve 1 g brucine sulphate and 0.1 g sulphanilic acid in about 70 mL of hot distilled water. Add 3 mL conc. HCl, cool and make up to 100 mL. This is stable for several months.
- Sulphuric acid solution: Carefully add 500 mL conc. H2SO4 to 125 mL distilled water and cool to room temperature.
- Sodium chloride solution: Dissolve 300 g NaCl and dilute to 1litre with distilled water.
- Sulphanilamide reagent: Dissolve 5 g sulphanilamide in a mixture of 50 mL conc. HCl and about 300 mL distilled water. Dilute to 500 mL with distilled water.
- N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine dihydrochloride solution: Dissolve 500 mg dihydrochloride in 500 mL distilled water. Store in a dark bottle.
- Hydrochloric acid: HCl (1+3)
- Stock nitrite solution: Dissolve 1.232 g NaNO2 in nitrite free water and dilute to 1 litre. Fresh nitrite from bottle should be taken 1 mL = 250 mg N in the solution. Preserve with 1 mL chloroform.
- Standard nitrite solution: Standardise stock solution. Pipette 50 ml standard 0.05 N KMnO4, 5 mL conc.H2SO4 and 50 mL stock nitrite solution in a glass stoppered flask. Discharge the permanganate colour by ferrous ammonium sulphate solution of 0.05 N (19.607 g ferrous ammonium sulphate and 20 mL conc.H2SO4 in 1 litre) strength. Carry nitrite free blank through the entire procedure and make necessary corrections. Calculate the nitrite N content of stock solution by the following equation:
- A = mg/mL nitrite N in stock solution,
- B = total mL standard KMnO4 used,
- C = normality of KMnO4 solution,
- D = total mL of standard Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2 used,
- E = normality of standard Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2,
- F = mL of stock NaNO2 solution taken for titration.
- Digestion reagent: Dissolve 134 g K2SO4 in 650 mL ammonia free distilled water and 200 mL conc.H2SO4. Add with stirring a solution prepared by dissolving 2 g red mercuric oxide (HgO) in 25 mL 6N H2SO4. Dilute the combined solution to 1 litre.
- Sodium hydroxide-sodium thiosulphate reagent: Dissolve 500 g NaOH and 2 g Na2S2O3.5H2O in ammonia free distilled water and dilute to 1 litre.
- Borate buffer solution: Add 88 mL 0.1N NaOH solution to 500 mL 0.025 M sodium tetraborate (Na2B4O7) solution (5 g Na2B4O7 in 1 litre) and dilute to 1 litre.
- Sodium hydroxide 6 N: Dissolve 240 g NaOH in 1 litre ammonia free distilled water.
- Standard iodine 0.1 N: Dissolve 40 g KI in 25 ml distilled water, add 13 g resublimed iodine and stir until dissolved. Transfer to 1 litre volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
- Standard fluoride solution: Dissolve 221 mg anhydrous sodium fluoride in distilled water and dilute to 1 litre. 1 mL = 100 µg F. This is the stock solution. Pipette 100 mL stock solution and make it up to 1 litre with distilled water to obtain standard solution 1ml = 10 µg F.
- Zirconyl-alizarin reagent: Dissolve 300 mg zirconyl chloride octahydrate (ZrOCl2.8H2O) in 50 mL distilled water contained in 1 litre glass stoppered volumetric flask. Dissolve 70 mg of 3-alizarin sulphonic acid sodium salt (also called alizarin red S) in 50 mL distilled water and pour slowly into the zirconyl solution while stirring. The resulting solution clears on standing for a few minutes.
- Mixed acid solution: Dilute 101 mL conc. HCl to approximately 400 mL with distilled water. Add carefully 33.3 mL conc. H2SO4 to approximately 400 mL distilled water. After cooling, mix the two acids.
- Acid-zirconyl-alizarin reagent: To the clear zirconyl-alizarin reagent in 1 litre volumetric flask, add the mixed acid solution and distilled water to the mark and mix. The reagent changes in colour from red to yellow within an hour.
KMnO4 = 4.55 ÷ Normality of KMnO4mL
To this solution add 2 to 3 mL concentrated H2SO4 and sodium bisulphite solution (10 g NaHSO3 + 100 mL distilled water). Boil to remove excess SO2, cool and dilute to 1000 mL with distilled water.
Sulphide
Residual chlorine (OTA)
Acidity
Ammonia N
Nitrate N
A = [(B x C) - (D x E)] x 7/F
where,
Each 1 mL of 0.05 N KMnO4 consumed by the nitrite corresponds to 1.729 µg NaNO2 or 350 µg N.
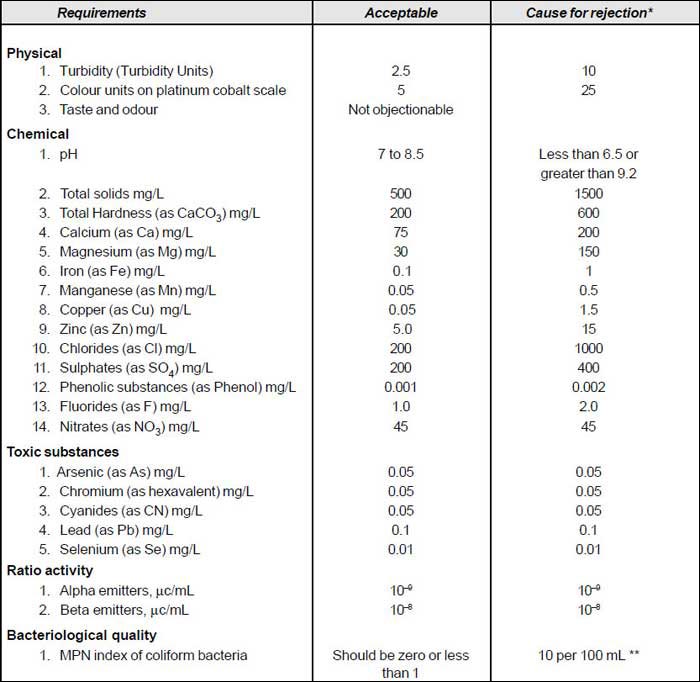
Standard of Drinking Water
*Figures in excess of the permissive while not acceptable may still be tolerated in the absence of alternative and better sources, but up to the limits designated, above which the supply will not be acceptable.
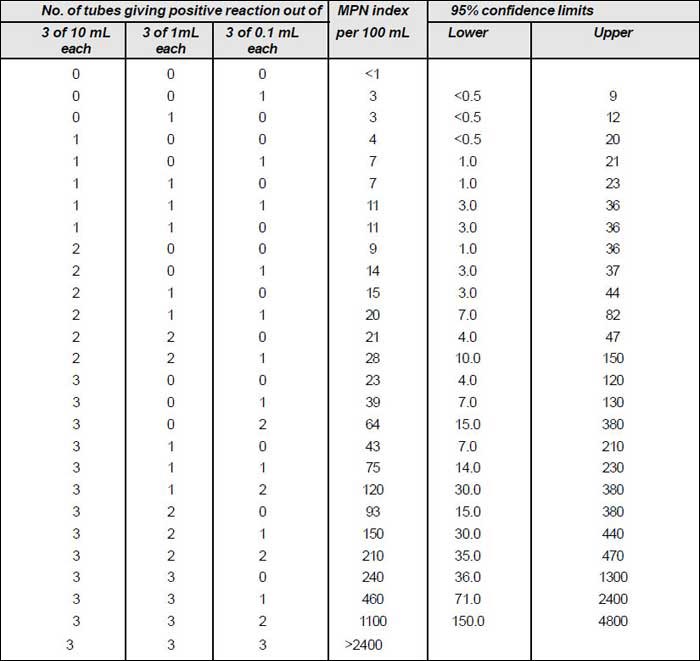
MPN Table
- If instead of portions of 10, 1 and 0.1 mL, a combination of 100,10 and 1 mL is used then the MPN is recorded as 0.1 times the value given in the table.
- For 1, 0.1 and 0.01 combination then 10 times the value in the table should be used.
- For 0.1, 0.01 and 0.001 combination, 100 times the value given in the table should be used.