Genetics of Diazotrophs
Nod Genes
Nodule forming species of Rhizobium consists of an extremely, large plasmid known as 'megaplasmid' in cell which possesses numerous genes coding for nodulation (nod genes) and nitrogen fixation (nif genes) (Rosenberg et al 1981). Both nod genes and nif genes are closely located. However, a physiological map of 135 Kb segment of megaplasmid was established which contained nod-nif regions.
The identified nod gene region is of 11.5 Kb in length. Nucleotide sequence and proteins encoded by 8.5 Kb fragment in E. coli has been determined. The nod genes consisted of 4 genes designated as nod A, B, C and D; the 4 genes code for proteins of 196, 217, 402 and 311 amino acid residues, respectively. Based on comparisons of nucleotide and amino acid sequences of nod A, B and C genes and amino acid sequence of nod A, B and C genes between different species of Rhizobium, about 69-72% homologous region has been characterized which is known as "common nod genes'' (Kondorosi et al., 1982).
Nif Genes
A region lies on genetic material of free living and symbiotic N2 fixers which consists of nitrogen fixing nif genes. In Rhizobium leguminosarum, R, meliloti and other species nif genes are located on a megaplasmid adjacent to nod genes, whereas in cyanobacteria e.g. Anabaena 7120 and most of free living bacteria nif genes are localized on the chromosome. Early studies on nif genes were carried out in Klebsiella pneumoniae and the function was confirmed by transferring into E. coli cells. Thereafter, nif genes in Rhizobium, cyanobacteria and other N2 fixers were discovered.
Researches were done on physical mapping to know the product of nif gene cluster. It was found that there are several parts of nif genes forming a gene clusture of 24 Kb nucleotides which are located between the genes encoding for histidine (his) and shikimic acid (shi A).
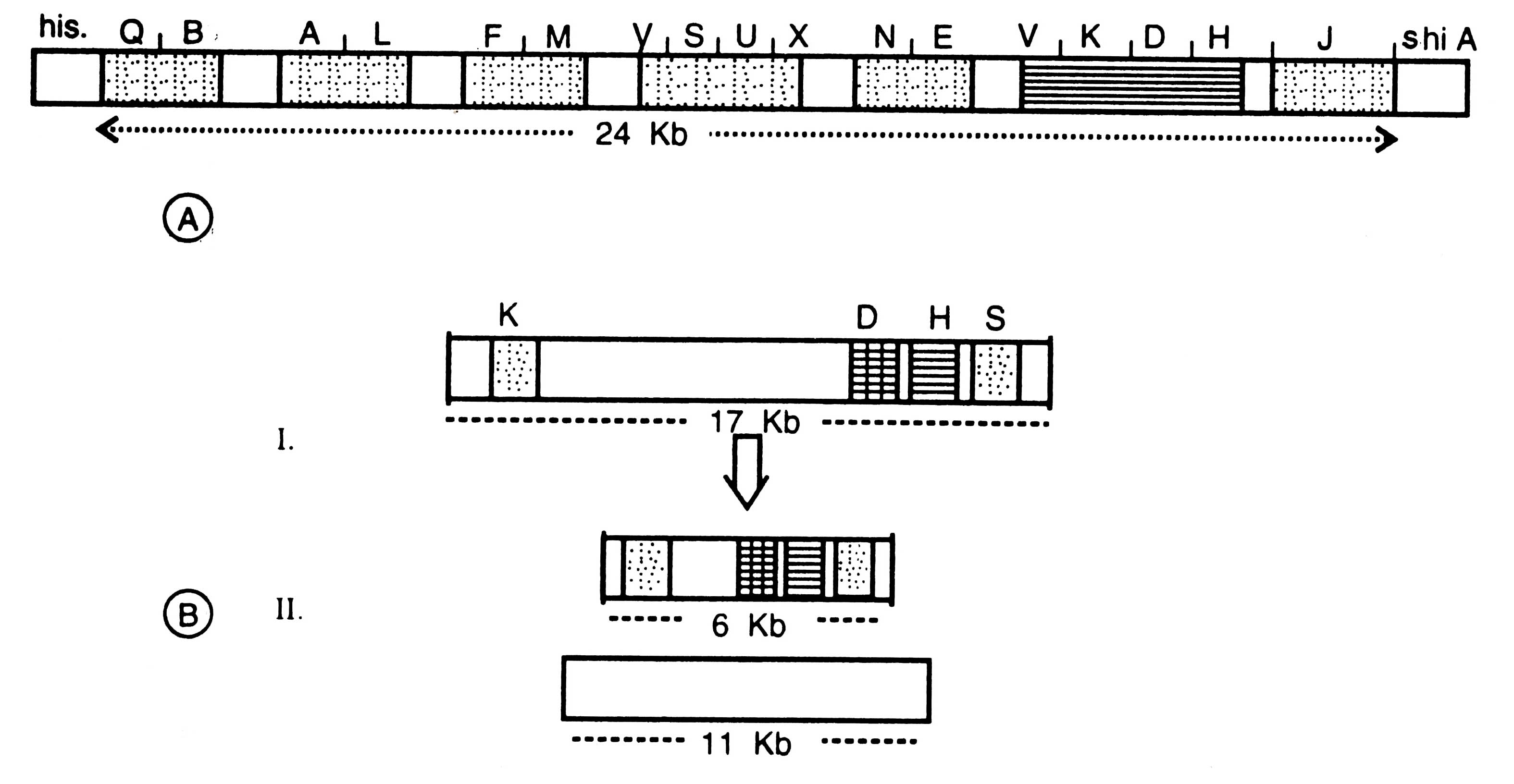
Fig. 11.8. A diagram of nif gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae (A) and Anabaena sp. (B). I-nif genes in vegetative cells; II-nif genes in heterocyst after rearrangement.
This cluster is organized in 7 operons i.e. transcription units (e.g. QB AL FM VSUX NE YKDH J). On the basis of mutational studies performed in all m/genes, the nature of various products of nif genes was determined. Now it is confirmed that nif HDKY operon encodes nitrogenase, whereas nif LA has regulatory function. In nif HDKY genes H, D and K encode for subunit of Fe-protein, Mo-Fe-Protein.
Nitrogenase acts only in the absence of ammonia and other nitrogen compounds as they inhibit its expression. Glutamine synthatase (GS) also losses its function. Glutamine synthatase gene encodes GS enzymes which is quite apart from nif genes.
Some filamentous cyanobacteria are composed of entirely vegetative cells (Golden et al, 1987). In absence of combined nitrogen source some photosysthetic vegetative cells differentiate into heterocysts at regular intervals along the filaments, terminal or lateral singly or in chains. In heterocysts, during differentiation many morphological, biochemical and genetical changes occur. At this time induction of nitrogenase takes place.
Organization of m/genes of vegetative cells and heterocysts was compared. It was found that in heterocysts the nifK and nifW were closely attached; size of nif gene cluster reduced from 17 Kb (in vegetative cell) to 6 Kb (in heterocyst) (Fig. 11.8B). This was proved by hybridizing the m/gene fragment with some of the m/gene probes by using restriction enzymes (Golden et al 1987).
Elmerich (1987) reviewed the N2 fixing organisms associated with nonleguminous plants and described the presence of plasmids of various molecular weight in Anabaena, Azotobacter, Frankia and Rhizobium.
In many countries researches on m/gene transfer into higher plants, especially in monocots, and gene expression in them are in progress. However, success has been made in m/gene cloning into E. coli. Since nif genes are prokaryotic in origin, the best strategy of their transfer into non-leguminous crops would be to transfer m/genes into chloroplast. The transcriptional and translational machinery of chloroplast bears several prokaryotic features. These attempts would be successful because the chloroplasts are geared to the production of ATP and reducing power, as both of which are required for nitrogen fixation (Merrick and Dixon, 1984). But the major problems for doing so are (i) lack of chloroplast transferring techniques, and (ii) protection of nitrogenase from O2 evolved during photosynthesis. Some more aspects of nif gene cloning have been discussed elsewhere (see Enzyme engineering and Trasnfer of nif genes to eukaryotes).
Hup Genes
In some species of Rhizobium, hydrogen uptake (or Hup) genes have been reported which displayed the ability to recycle H2 (produced as a result of conversion of N2 to NH3) back to nitrogenase complex. This mechanism helps the plant to harvest the energy as being lost by the plants (Fig. 11.2).




