Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
-
Number of adenine molecules always equaled number of thymine molecules.
-
Number of cytosine molecules always equaled number of guanine molecules.
-
Number of adenine molecules did not necessarily equal that of guanine and similar relationship was observed between cytosine and thymine.
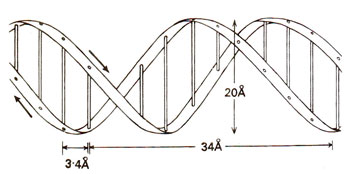
Besides chemical analysis, DNA was also studied by X-ray crystallography by M.H.F. Wilkins and his associates. Such studies demonstrated that DNA was a helical structure with a diameter of 20 Å and a pitch (one round) of about 34 Å. On the basis of these studies of chemical analysis and X-ray crystallography, following features of the DNA molecule are now known:
-
DNA consists of a double helix, in which two polynucleotide chains are coiled about the same axis in such a fashion that they can separate from one another only by uncoiling andthat lateral separation would not be possible.
-
Bases are set in a plane at right angle to the long axis.
-
Two polynucleotide chains which run in opposite directions have complementary base : sequences, since adenine is linked to thymine and cytosine to guanine.
-
Distance between two base pairs is 3.4 Å and there are 10 base pairs in each turn.
Choice of base pairing is understandable because of a constant diameter of 20 Å in the molecule; two purines would need too much space and two pyrimidines would occupy too little space to pair. When a pyrimidine always pairs with a purine, space could remain constant. The pattern of coiling of two polynucleotide chains is shown in' Figure 25.15.