Genetics / Chemistry of the Gene / Nucleic Acids and Their Structure
Nucleotides
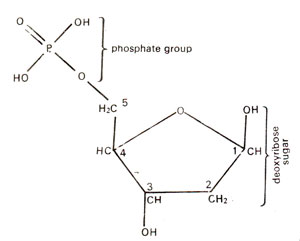
Fig. 25.11. A deoxyribosc sugar molecule linked with phosphate group at 5' position.
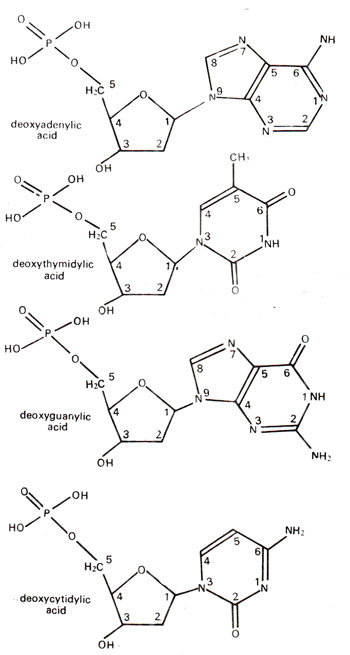
Fig. 25.12. Structures of four different 5'p 3' OH nucleotides found in DNA.
A nucleotide is derived from a nucleoside by addition of a molecule of phosphoric acid. The phosphate molecule is linked with sugar molecule at carbon no. 5 (Fig. 25.11) or at carbon no. 3. Correspondingly nucleotides will be called 5'p3' OH nucleotide and 3'p5' OH nucleotide. In case of ribose, the phosphate group may be linked even at carbon no. 2 of ribose sugar, because hydroxyl group is available at position no. 2 also. However, in biological systems nucleotides have phosphate cither at 5' position or at 3' position. The four nucleotides found in DNA are (i)
deoxycytidylic acid or
deoxycytidylate, (ii) deoxythymidylic acid or
deoxythymidylate, (iii)
dexoyadenylic acid or
deoxyadenylate and
(iv) deoxyguanylic acid or
deoxyguanylate. The structures of these four nucleotides are shown in Figure 25.12. Similarly, the four nucleotides found in RNA are (i)
cytidylic acid or
cytidylate, (ii) uridylic acid or
uridylate, (iii)
adenylic acid or
adenylate and
(iv) guanylic acid or
guanylate.

Fig. 25.11. A deoxyribosc sugar molecule linked with phosphate group at 5' position.

Fig. 25.12. Structures of four different 5'p 3' OH nucleotides found in DNA.
Support our developers

More in this section








