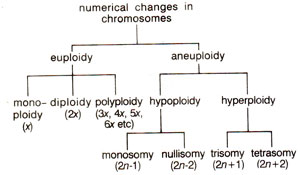
Fig. 20.1. Different kinds of numerical changes in chromosomes (x = basic chromosome number; 2n = somatic chromosome number).
Numerical changes in chromosomes or variations in chromosome number
(heteroploidy), can be mainly of two types, namely (i)
aneuploidy and
(ii) euploidy. Aneuploidy means presence of chromosome number which is different than a multiple of basic chromosome number. Euploidy, on the other hand, means that the organism should possess one or more full sets of chromosomes.
Let us imagine that 7 is the basic chromosome number (
x)in a particular class of individuals where diploid number (
in) is 14. In this case, chromosome numbers 2
n = 15 and 2
n = 13 would be aneuploids, while those having 2
n = 7, 21, 28, 35 or 42 would be euploids. A classification of different kinds of numerical changes in chromosomes is presented in Figure 20.1.

Fig. 20.1. Different kinds of numerical changes in chromosomes (x = basic chromosome number; 2n = somatic chromosome number).

