Gene Expression
The DNA has two important roles in the cell, first is replication and the second is expression. Gene expression accomplished by a series of events that contained in DNA is converted into molecule that take place in the cell. The information contained in DNA is converted into molecules that determines the metabolism of the cell. During the process of gene expression DNA is first copied into an mRNA molecule which determines the amino acid sequence of a molecule of protein. The RNA molecules are synthesized by using a portion of base sequences of single strand of double stranded DNA. This single strand is called template. Hence formation of an RNA transcript is facilitated by an enzyme RNA polymerase. Therefore, the process of synthesis of an RNA molecule corresponding to a gene is called transcription. By using base sequences and RNA molecule proteins are synthesized in a definite order. Production of an amino acid Sequence from an mRNA base sequence is called translation. After completion of translation proteins are synthesized. Therefore gene expression refers to proteins synthesis through two major events, transcription and translation.
Central Dogma
DNA itself cannot directly order for the synthesis of amino acids but forms its transcripts first which is then translated into protein. For the first time in 1958, F. Crick suggested that there is unidirection flow of informations from DNA to RNA to protein shown as below:
| DNA |
Transcription |
RNA |
Translation |
Protein |
 |
 |
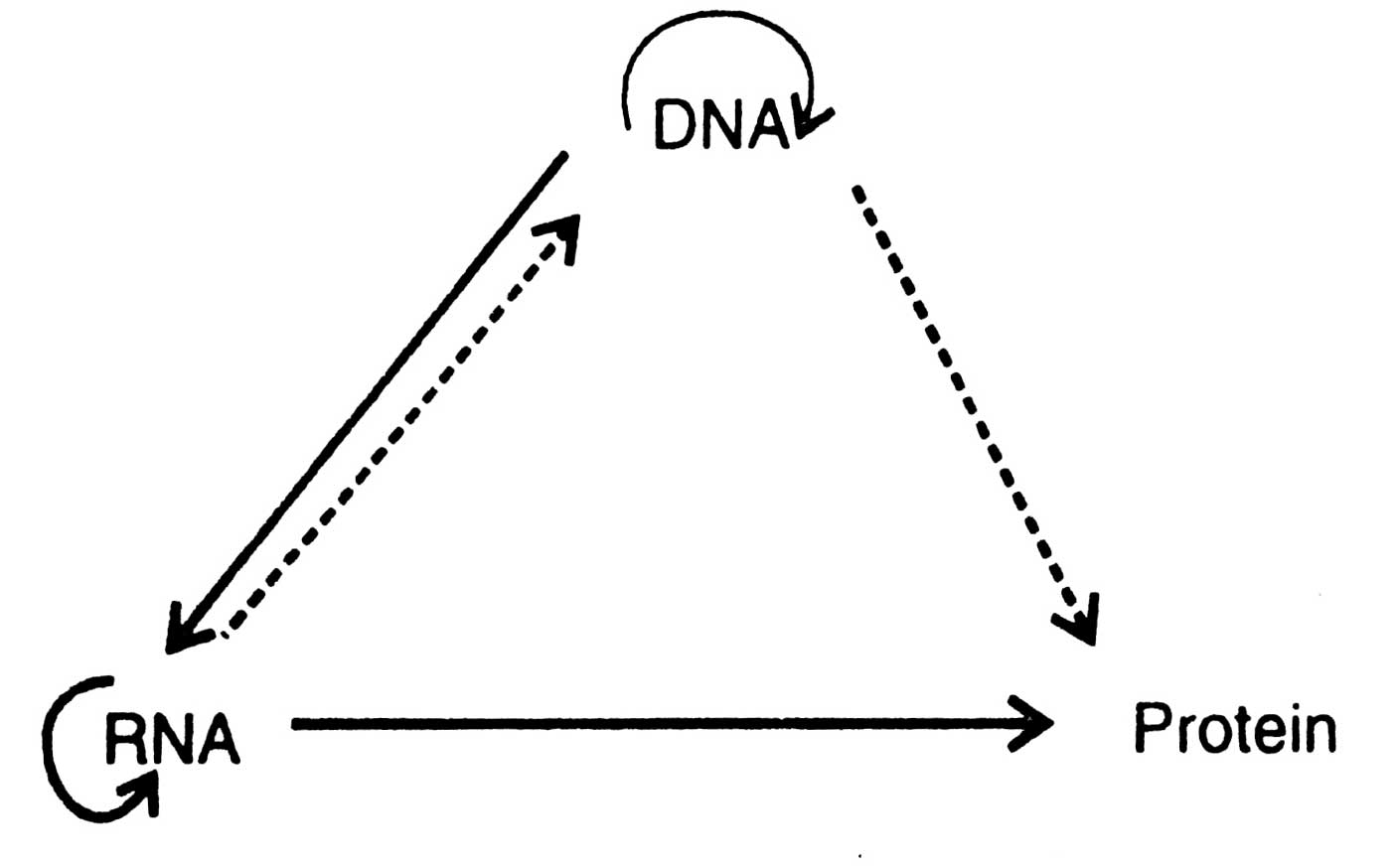
Fig 2.10. Modified central dogma i.e. RNA dependent DNA synthesis
This sequential transfer of information from DNA to protein via RNA is known as
central dogma. Further more in 1963 H.M. Temin and coworkers reported that Rous sarcoma virus causing cancer contains RNA as genetic material. In1964, he put forward a hypothesis that RNA tumour viruses synthesize an enzyme reverse transcriptase that synthesized DNA from RNA template. It could also be demonstrated that DNA synthesis prevented after destroying enzyme RNase. It was also shown that RNA specific DNA was synthesized. However, in lymphocytes of leukemia patients RNA-dependent DNA polymerase was discovered. In 1970 Crick again suggested a modified version of central dogma (Fig.2.10).
DNA can undergo replication process to form DNA and transcription to form RNA that in turn undergoes translation. RNA also replicates to form RNA. . In special cells only (dot lines) RNA synthesizes DNA, and DNA synthesizes proteins.
This process is known as RNA directed DNA synthesis (Temin, 1972). For detailed discussion of transcription and translation see
A Text Book of Microbiology by Dubey and Maheshwari (1999).





