Genetics / Sex Determination, Sex Differentiation, Dosage Compensation and Genetic Imprinting
Diploid intersexes in gypsy moth (Lymantria)
Incase
of Drosophila, intersexes have to be triploid or tetraploid and not diploid. Therefore, any diploid intersexes known, cannot be explained due to a balance between autosomes and X-chromosomes. These would instead be explained due to a quantitative balance between male and female determining factors. Such diploid intersexes are known in gypsy moth (
Lymantria dispar)and were discussed extensively by R.B. Goldschmidt in 1936 and 1955. It was established that such diploid intersexes are obtained due to presence of different grades of sex factors varying from strong to weak. It was also demonstrated in gypsy moth that sex chromosomes from different geographical races carry sex factors of different strengths. This disturbs the balance of sex in hybrids obtained due to crosses between different races. Diploid intersexes are thus produced.
In gypsy moth, female sex is heterogametic (FM) and male is homogametic (MM). A European race was found to be weak, so that female Europeans were designated as FwMw and male Europeans as MwMw., This means that Fw chromosome of weak race can overcome male determining factors in Mw to produce a normal female. Similarly in strong Japanese race, females are FsMs and males are MsMs. Crosses between males and females of same race give males and females in equal proportions. However, if weak and strong races were intercrossed, different results were obtained in reciprocal crosses (Figs. 17.8, 17.9). It is obvious that in a cross between weak European female (FwMw) and strong Japanese male (MsMs), intersexes (FwMs) are obtained (Fig. 17.8), because Fw can not overcome the male factors in Ms. In the reciprocal cross between strong Japanese female (FsMs) and weak European male (MwMw), no intersexes are obtained (Fig. 17.9).

Fig. 17.8. In gypsy moth, results of a cross between a weak European female (FwMw) and a strong Japanese male (MsMs)
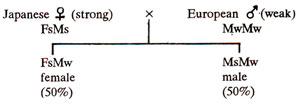
Fig. 17.9. In gypsy moth, results of a cross between a strong Japanese female (FsMs)and a weak European male (MwMw).
Support our developers

More in this section