Amino acid content of proteins
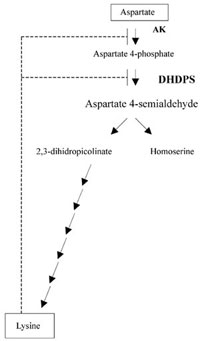
Biochemical regulatory mechanism proposed to regulate the synthesis of the amino acid Lysine, in higher plants, derived from the amino acid Aspartate. Enzyme activities, aspartate kinase (AK) and dihidrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) are indicated. Broken lines indicate the inhibition of these enzymes by Lysine.

Biochemical regulatory mechanism proposed to regulate the synthesis of the amino acid Lysine, in higher plants, derived from the amino acid Aspartate. Enzyme activities, aspartate kinase (AK) and dihidrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) are indicated. Broken lines indicate the inhibition of these enzymes by Lysine.
The strategyconsistedof the integrationin the genomeof soybeanof genes from otherspeciesencodingfor enzymeswithout thefeed-backmechanism. The transformation of soybeanwith the gene lysCM4 from Escherichia coli (encodingAK) andthe dapA genefrom Corynebacterium (encodingDHDPS), both insensitiveto the feed-backinhibition by lysine, resultedin a transgenic soybeanplant with a duplicatedpathwayof lysine biosynthesis,one sensitive and the other insensitive to lysine. As a result, the lysine content of the transgenicsoybeanplants was over 100-fold the value of the untransformed plants.Other plant specieslike corn, wheatandcanolahavebeensubjectedto the samegenetic manipulationto increasetheir lysine content with similar resultsto thoseobtainedin soybean.




