Organic Molecular Structure of Living Systems
Organic Molecular
Structure of Living Systems
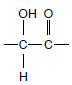
Chemical evolution in the prebiotic environment produced simple organic compounds that ultimately formed the building blocks of living cells. The term “organic compounds” refers broadly to compounds that contain carbon. Many also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, salts, and other elements. Carbon has a great ability to bond with other carbon atoms in chains of varying lengths and configurations. Carbon-to-carbon combinations introduce the possibility of enormous complexity and variety into molecular structure. More than a million organic compounds have been identified.
We review the kinds of organic molecules found in living systems, followed by further discussion of their origins in earth’s primitive reducing atmosphere.
Chemical evolution in the prebiotic environment produced simple organic compounds that ultimately formed the building blocks of living cells. The term “organic compounds” refers broadly to compounds that contain carbon. Many also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, salts, and other elements. Carbon has a great ability to bond with other carbon atoms in chains of varying lengths and configurations. Carbon-to-carbon combinations introduce the possibility of enormous complexity and variety into molecular structure. More than a million organic compounds have been identified.

We review the kinds of organic molecules found in living systems, followed by further discussion of their origins in earth’s primitive reducing atmosphere.




