Amniocentesis and antenatal diagnosis
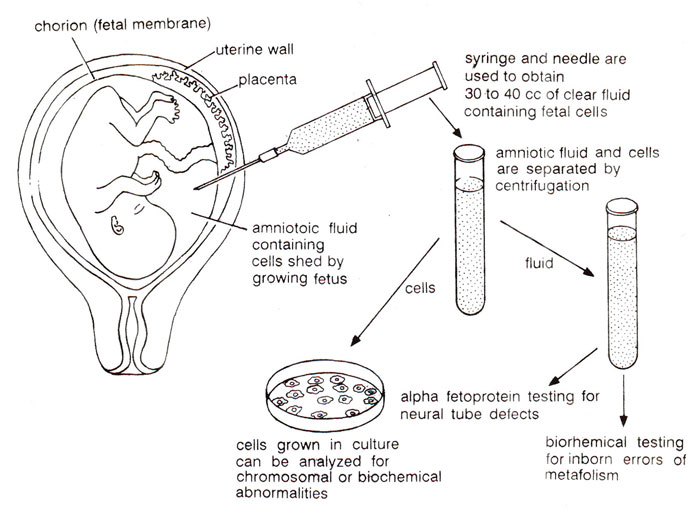
Fig. 24.8. Technique of amniocentesis, used to test for hereditary or developmental defects in the fetus.

Fig. 24.8. Technique of amniocentesis, used to test for hereditary or developmental defects in the fetus.
It is possible to identify the disease now within 2 months of pregnancy, unlike an 18 week period required earlier. The number of disease specific DNA probes is also increasing at a fast rate, so that antenatal diagnosis by DNA analysis or linkage should be possible for all single gene defects. In recent years, the incidence of the disease thailassaemia in Cypriot community in Britain has fallen from 30 to 2 per year, due to the use of antenatal diagnosis. In U.S.A. on the other hand, there is a campaign against abortion and, therefore, also against antenatal diagnosis. In such cases there will be births of defective children and these may become patients for gene therapy discussed in the following section.




