Molecular Biology of Plant Pathways / Engineering Plant Alkaloid Biosynthetic Pathways
Tetrahydrobenzylisoquinoline Alkaloids
The opium poppy
P. somniferum contains more than 80 tetrahydrobenzylisoquinoline-
derived alkaloids. It is the source of the narcotic analgesics codeine and
morphine.
P. somniferum is one of mankind’s oldest medicinal plants, and the
plant as we know it today is the result of centuries of breeding. Our biochemical
and molecular genetic knowledge of
P. somniferum is relatively advanced.
We understand how morphine is enzymatically formed and cDNAs encoding
the enzymes occurring mainly downstream of formation of the first alkaloid in the
pathway, (S)-norcoclaurine, have been isolated (Kutchan, 1998). Our current
understanding of alkaloid biosynthesis in
P. somniferum is as follows.
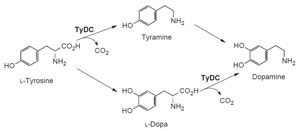 |
| FIGURE 10.5 Schematic representation of the
biosynthetic grid leading from L-tyrosine to
dopamine. tydc, tyrosine/dopa decarboxylase. |

