Determination of COD in Water
To determine the Chemical Oxygen Demand (C.O.D.) for given sample.
Principle
Potassium dichromate is a powerful oxidising agent in acidic medium and is obtained in high state of purity.
The reaction involved is:
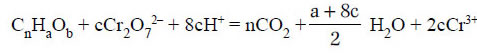
where, c = 2/3n + a/6 - b/3
- Reflux apparatus
- Burettes
- Pipettes
Reagents (click to check the preparation of reagents)
- Standard potassium dichromate solution 0.25N.
- Sulphuric acid reagent.
- Standard ferrous ammonium sulphate.
- Ferroin indicator solution.
- Mercuric sulphate.
- Sulphuric acid crystals.
- Place 50.0 mL of sample in a 500 mL refluxing flask.
- Add 1g mercuric sulphate and a few glass beads.
- Add sulphuric acid to dissolve the mercuric sulphate and cool.
- Add 25.0 ml 0.25 N potassium dichromate solution and mix well.
- Attach the flask to the condenser and start the cooling water.
- Add the remaining acid reagent (70 mL) through the open end of condenser and mix well.
- Apply heat and reflux for 5 hours.
- Cool and wash down the condenser with distilled water.
- Dilute the mixture to about twice its volume and cool to room temperature.
- Titrate the excess dichromate with standard ferrous ammonium sulphate using ferroin indicator (2 to 3 drops).
- The colour change from blue green to reddish indicates the end point.
- Reflux in the same manner a blank consisting of distilled water of equal volume as that of the sample.
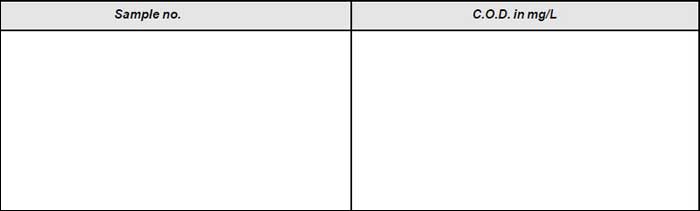
Observation
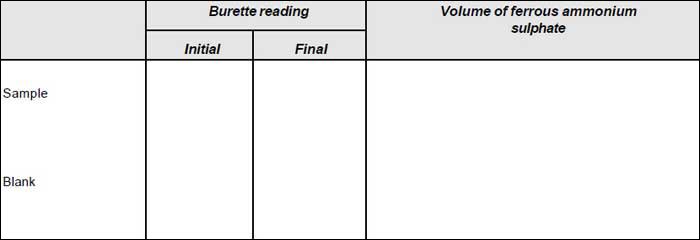
Calculation
| mg/L C.O.D. = | (V1 - V2) N x 8000 |
| V |
V1 = mL ferrous ammonium sulphate used for blank
V2 = mL ferrous ammonium sulphate used for sample
N = normality of ferrous ammonium sulphate
V = volume of sample used.
Results