Determination of Fluoride in Water
To determine the fluorides present in water.
Principle
Fluorides in excessive quantities and absence of fluorides in water, both create problems. A disfigurement in teeth of humans known as mottled enamel or dental fluorosis is occured in those, who consume waters with fluoride content in excess of 1.0 mg/L. It has been scientifically established that 0.8-1.0 mg/L of fluorides is essential in potable water. Thus, absence or low fluoride content may cause dental caries in the consumers.
Zr_alizarin lake + 6F (reddish colour) |
 |
alizarin + ZrF6-- (yellow |
The bleaching action is the function of the fluoride ion concentration and is directly proportional to it. Thus, Beer's law is satisfied in and inverse manner.
- Spectrophotometer or colour comparator
Reagents (click to check the preparation of reagents)
- Standard fluorides solution 1mL = 10µgF.
- Zirconyl-alizarin reagent.
- Mixed acid solution.
- Acid-zirconyl-alizarin reagent.
- Sodium arsenite solution.
Procedure
- If residual chlorine is present, remove the same by adding one drop of arsenite per 0.1 mg Cl and mix.
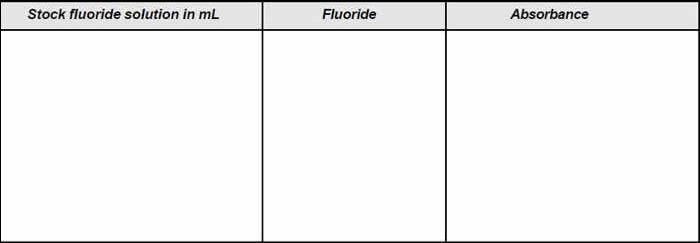
- Prepare a series of standard by diluting various volume of standard fluoride solution (1 ml =10 µgf) to 100 mL in tubes. The range should be such that it is between 0 and 1.4 mg/L.
- To 50 mL of each standard add 10 mL mixed acid-zirconyl-alizarin reagent.
- Set the spectrophotometer to a wavelength of 570 nm.
- Adjust the spectrophotometer to zero absorbance with the reference solution i.e., distilled water with reagent.
- Plot the concentration along x-axis and absorbance along y-axis and obtain a calibration curve.
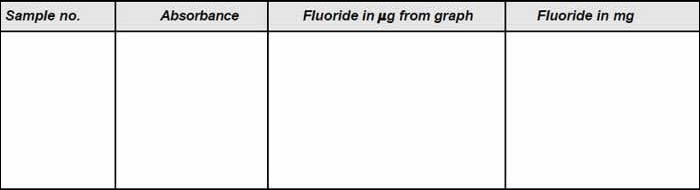
- Take 50 mL of the sample and add 10 mL of mixed acid-zirconyl-alizarin reagent and mix well.
- Place the solution in the spectrophotometer and read the absorbance.
- By referring the calibration curve, the concentration for the observed absorbance is read out.
- Repeat the procedure with dilute samples.
Observation
The observation is presented in Tables A and B respectively.
Table A: Observation for calibration
Calculation
| F in mg/L = | A x B |
| V x C |
A = μgF determined
B = sample dilute to this volume
C = portion taken for colour development
V = mL of sample.
Results