Chemistry Lab Protocols / Classical techniques
Types of ligand
Ligands are chemical species that co-ordinate with metal ions to form a
complex. They are classified on the basis of the number of points of
attachment to the central ion.
- Monodentate ligand - here the ligand is bound to the central ion at only
one point, e.g. H2O, NH3.
- Bidentate ligand - this has two points of attachment to the central ion,
e.g. ethylenediamine (en) (Fig. 23.1).
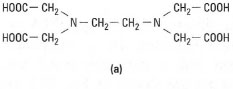
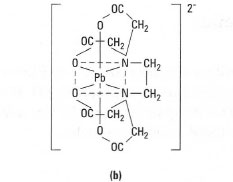
- Multidentate ligand - these have several points of attachment, e.g.
ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid (EDTA), which is a hexadentate ligand
(six points of attachment) (Fig. 23.2).
![Structure of [Co(en)3]3+. It is a six co-ordinate octahedral complex of ethylenediamine (en) with cobalt (III).The complex has three five membered rings.](images/23.1.jpg) |
| Fig. 23.1 Structure of [Co(en)3]3+. It is a six co-ordinate octahedral complex of ethylenediamine (en) with cobalt (III).The complex has three five membered rings. |
|
| Fig.23.2 Structure of EDTA. (a) EDTA contains two donor N atoms and four donor 0 atoms. It can therefore form a hexadentate complex (b) with a metal ion, e.g. Pb2+. |
Support our developers

More in this section
![Structure of [Co(en)3]3+. It is a six co-ordinate octahedral complex of ethylenediamine (en) with cobalt (III).The complex has three five membered rings.](images/23.1.jpg)