Medicinal Plants | Alkaloids
Alkaloids Derived from Anthranilic Acid
Anthranilic acid (Figure 106) is a key intermediate
in the biosynthesis of L-tryptophan and so contributes to the elaboration of indole alkaloids. During this conversion, the
anthranilic acid residue is decarboxylated, so that
only the C6N skeleton is utilized. However, there
are also many examples of where anthranilic acid
itself functions as an alkaloid precursor, using processes
which retain the full skeleton and exploit
the carboxyl (Figure 106). It should also be appreciated that, in mammals, L-tryptophan can be degraded back to anthranilic acid , but this is not a route of importance in plants. |
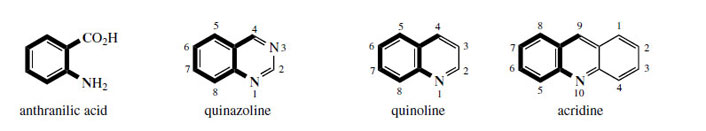 |
| Figure 106 |
Support our developers

More in this section





