Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Pneumonia
| Purpose | To identify bacterial species in a simulated sputum as quickly as possible |
| Materials | Simulated sputum in a screw-cap container, accompanied by a laboratory request for culture
Mannitol salt agar plate (MSA) Dropping bottle containing 3% hydrogen peroxide Tubed plasma (0.5-ml aliquots) Sterile 1.0-ml pipettes Pipette bulb or other aspiration device |
Procedures
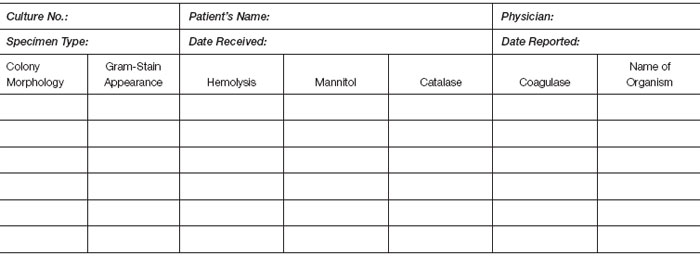
- Make a Gram stain of the simulated sputum specimen. Record the results and place the information on your work card.
- With your sterilized inoculating loop, inoculate a blood agar and a mannitol salt agar plate. Streak each for isolation of colonies. Incubate both plates at 35°C for 24 hours.
- When the “physician” calls, refer to your work card and give him or her specific information about your microscopic interpretation of the Gram-stained smear.
- After the plates have incubated, examine each carefully. Record colonial morphology on the work card, and make Gram stains of different colony types on each medium.
- Perform the catalase test on different colony types on each medium. Be careful not to scrape the surface of the blood agar plate or a false-positive reaction will occur.
- Perform the coagulase test with any colony on either plate that appears to be a Staphylococcus.With a sterilized inoculating loop, pick up a colony and emulsify it directly in 0.5 ml of plasma. Incubate the plasma tube and read at intervals from 30 minutes to 4 hours. If necessary, incubate the tube overnight and read the result the next day. Record the result on your work card.
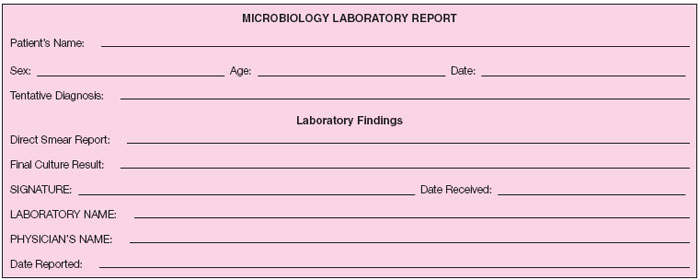
- Prepare a final report for the “physician.”
Results
- Laboratory work card (record of your work to be kept on file at least two years).
- Final laboratory report to “physician.”
 |




