Staphylococci in the Normal Flora
| Purpose | To isolate and identify staphylococci in cultures of the nose and hands |
| Materials | Blood agar plates (BAP) Mannitol salt agar plates (MSA) Sterile swabs Dropping bottle containing hydrogen peroxide Tubed plasma (0.5-ml aliquots) Latex agglutination kit for Staphylococcus aureus |
Procedures
- Take a culture of your own nose by swabbing the membrane of one of your anterior nares with a sterile swab.
- Inoculate the nasal swab across the top quarter of a blood agar and a mannitol salt agar plate. Streak across the remainder of each plate for isolation of colonies. Discard the swab in disinfectant.
- Take a culture from the palm of your left hand by swabbing across it. Inoculate a blood agar and a mannitol salt agar plate and streak for isolation of colonies.
- Sterilize your inoculating loop and moisten it in sterile saline. Run the moistened loop under one of your fingernails, picking up some debris if possible. Inoculate a blood agar and a mannitol salt agar plate and streak out.
- Incubate all plates at 35°C for 24 hours.
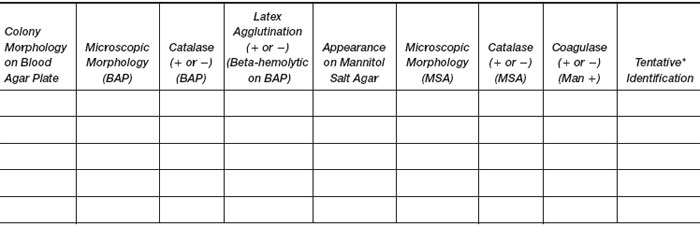
- Examine the plates and make Gram stains of different colony types on both the blood and mannitol plates. Perform a catalase test on the different colony types on both blood and mannitol plates by smearing a small amount of colony growth onto a slide and with a capillary pipette, placing one drop of hydrogen peroxide onto each smear. Be careful not to dig into the blood agar medium or a false-positive result may be obtained. Observe for bubble formation (refer to fig. 18.1). Perform a coagulase test on a colony of mannitol-positive staphylococci, if present, using your loop to pick it from an MSA plate and emulsify it directly in 0.5 ml of plasma (continue as in Experiment 20.1, steps 6c and d). Perform a rapid latex agglutination test on any beta-hemolytic colonies that show gram-positive cocci in clusters on Gram stain.
- Record your observations in the following table.
Results
 |




