Thermogravimetry
The apparatus required for TG analysis is shown in Fig. 36.1. TG is normally carried out on solid samples. Example operating conditions are as follows:| Sample: Crucible: Rate: Atmosphere: Mass: |
calcium oxalate monohydrate platinum pan 10 K min−1 nitrogen, 20 mL min−1 10.5 mg |
The result can be expressed as either a TG curve, a plot of changing weight with respect to temperature or time, or a derivative of the curve, i.e. DTG, where the first derivative of the TG curve is plotted with respect to temperature or time. As well as providing information on the thermal decomposition of inorganic compounds, additional information can be deduced, e.g. sample purity and Mr
The oxalate hydrates of the alkaline earth metals, e.g. calcium, strontium and barium, are all insoluble. If a calcium salt made acidic with ethanoic acid is treated with sodium oxalate solution, a white precipitate of calcium oxalate monohydrate is formed quantitatively. After washing the precipitate with ethanol it can be analysed. A typical TG curve, for calcium oxalate monohydrate, CaC2O4.H2O, is shown in Fig. 36.2. Box 36.1 shows how to interpret a thermal analysis trace for calcium oxalate monohydrate.
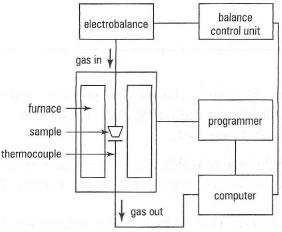 |
| Fig. 36.1 Schematic diagram of a system for thermogravimetry. |
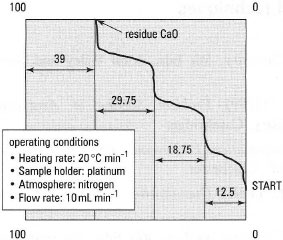 |
| Fig. 36.2 A typical thermal analysis trace for CaC2O4.H2O. |




